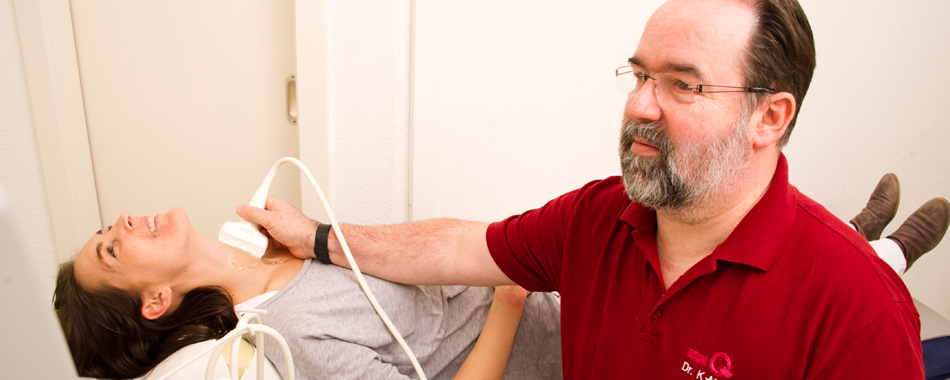
Sonography
An ultrasound examination (sonography) is a method involving absolutely no radiation exposure that can be even applied in pregnant women. The principle of sonography is based on the application of ultrasonic waves within the non-audible range. The examining doctor obtains two-dimensional live images depicting the size, form and structure of the area to be examined on a monitor. An ultrasound examination requires an experienced diagnostician, due to the fact that the quality of the examination results depends greatly on the examining doctor.
- The ultrasound examination method works especially well in the areas, where soft tissues prevail and no bones are in the way.
- In cancer diagnostics, it is, for example, possible to detect liver metastases or identify cysts in the liver.
- In the area of soft tissues of the neck, thyroid gland and kidneys, sonography is very significant.
- With the help of the special ultrasonic probes, mamma sonography is an excellent complement to mammography and, if required, is also suitable for the collection of tissue samples.
How is the examination performed?
Depending on the region to be depicted, the patient is placed accordingly. For example, to perform the examination of the abdominal cavity, the patient mostly lies on his back. The doctor applies a clear water-based gel to the skin. If the transducer is pressed to the skin without a gel, the ultrasonic waves will be completely reflected because of the air between the transducer and the skin. In this way the doctor would not obtain any images. Due to the moving and angling of the transducer on the skin, the doctor can see the organs and tissues of concern from different directions. On completion of the examination, which takes about 5 to 15 minutes, the gel can be wiped off.
Preparation for the examination
Normally, sonography does not require any preparation. Sometimes, in order to prepare for the upper abdominal sonography, you will be given a medicine that you should take a few hours before the ultrasound examination to reduce stomach swelling. The reason is that the intestinal loops filled with air interfere with the ultrasound by impairing image quality.